I. Background
The implementation of the New Senior Secondary English language Curriculum (NSSC) has commenced at Secondary 4 since September 2009. One major feature is that it comprises the Compulsory and Elective Parts. In addition to developing students’ basic language skills, the NSSC provides more variety and flexibility to cater for their varied interests, needs and abilities.
However, the Core and Elective Parts are not two separate and unrelated components in the NSSC. Educators often think that it is essential to achieve coherence in the curriculum because ‘lacking such coherence, the curriculum is likely to be little more than a smorgasbord of superficial, abstract, irrelevant, and quickly forgotten pieces.’ (Toward a Coherent Curriculum, p.4) Such coherence is reinforced by the complementary roles that the Core and the Elective Parts play in the NSS English language Curriculum, which are clearly set out:
| |
‘[the Electives] focus not so much on the explicit teaching of subject knowledge and skills (i.e. the four skills, grammar, communicative functions, vocabulary and text-types) as on providing learners with opportunities to apply them through following a particular approach or exploring a particular topic which may or may not be covered in the Compulsory Part.’ (English Language Curriculum and Assessment Guide, p.30) |
What can teachers do in their curriculum design to help realise such a principle? What possibilities are there in implementing the Core and Electives?
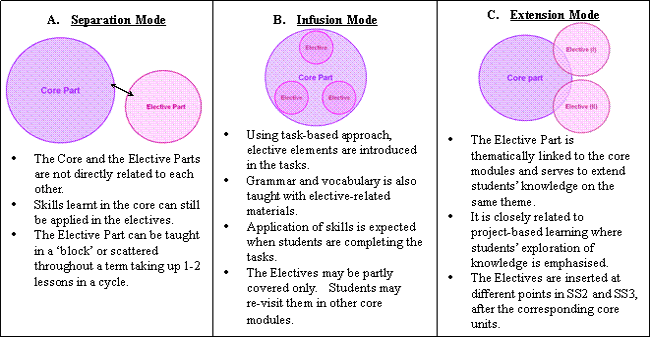
Given the flexibility of the NSSC, schools collaborating with the section have adopted different ways of organising the Core and the Elective Parts, which are illustrated in the following figures:
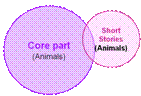
This study illustrated the extension mode further with a school example. In this school, the Short Stories elective and the core module share the same theme ‘Animals’. Short stories about animals are chosen for the elective module to extend students’ knowledge on the theme. |
 |
School Background
Many students in TWGHs Wong Fung Ling College lack motivation in learning English and most of them have no prior knowledge in the Short Stories elective module. Teachers have been working as a team for several years with a collaborative culture cultivated among them. They have had hands-on experience and materials in teaching the elective because they started infusing elements of the short stories elective in S2 in the year 08/09 to promote a smoother interface between the junior and senior secondary. With the commencement of NSS in the year 09/10, they are more aware of the need to make coherence among the various components in the English Language curriculum.
Level
S2
II. Strategies used
- Curriculum design
-
The elective serves as an extension to the core unit so that students can extend their knowledge on the theme ‘Animals’ and apply the skills they have learnt in the core unit.
-
Learning and teaching materials in both the Core and Elective Parts are thematically linked.
- Module design
-
In addition to linking the core and elective modules, coherence is achieved within the module by adopting task-based learning (TBL) approach, which promotes the integration of language skills development, grammar and vocabulary learning, as well as the process writing approach. The SBA component is also infused into the modules.
- Teaching and learning
-
Adaptations have been made to the course book materials in the Core Part to suit students’ abilities.
-
The elective module starts from the basics because students have no prior knowledge in short stories.
-
As students do not have a strong English foundation, there is more careful scaffolding for the tasks, and more motivating materials, like visual aids, are designed to support their learning.
-
Tasks are designed to help develop students’ generic skills, e.g. creativity, self-learning, collaboration and communication.
-
Assessment
|

