Tasks |
SDL-related features |
Artefacts |
| 1. |
Conducting an introductory session for junior form students to provide opportunities for them to reflect upon their learning needs and attitudes and set goals |
| - |
Students did a learning habit survey to analyse their own learning needs and attitudes. |
| - |
The teachers summarised the self-directed learning tasks planned for the new school year. Students then set their learning goals for the year based on the learning tasks suggested and other self-directed learning tasks they could devise for themselves. |
|
Developing ownership of learning |

Students getting to know more about their learning needs and attitudes

A student sharing his goals in self-directed learning
|
| 2. |
Selecting familiar topics to increase motivation |
| - |
Two units of work were developed for S1, S2 and S3 respectively. To improve learning interest, topics related to students’ daily and school lives were selected. |
|
Developing ownership of learning |
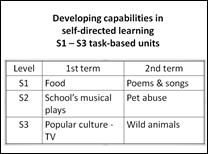
Topics related to daily life and school life
|
| 3. |
Activating prior knowledge and relating it to students’ daily life |
| - |
Students were given a KWL (What I know, what I want to know, what I have learned) chart. By asking them what they already knew, teachers could help them relate their prior knowledge to the topic so that they had more incentive to learn. |
| 4. |
Managing learning through an enquiry learning task |
| - |
After brainstorming what they wanted to know in the KWL chart, students surfed websites for relevant information on their own. Then they shared what they had learned with others. In the information seeking process, students determined and pursued their own lines of enquiry. They built on their prior knowledge and looked for information they needed. They evaluated and used the information for communicating their learning to others. |
|
Developing ownership of learning
Developing self-management skills |

A KWL chart on Western food and culture

Students surfing websites to learn more about Western food and culture
|
| 5. |
Preparing students to work on their own |
| - |
When moving on to senior forms, students need to manage more complex and integrated tasks. To prepare them to work on their own, the teachers introduced strategies which could be applicable to other tasks.
- Note-taking skills: As students need to listen to more complex information in senior forms, they improved information retention by learning more about note-taking. They learned what content words are, and learned to use short forms and create their own symbols.
- Pre-task questions: Many students do not study a question or topic before attempting it. The teachers set pre-task questions to prepare students better for a task. For example, they asked students to predict what information they needed to read or listen to in order to complete an integrated task. They also guided students to identify the key linguistic feature used, namely imperatives, when reporting a sequence of actions. (Sample 1) (Sample 2)
|
|
Developing self-management skills |

Learning commonly used symbols and creating own symbols for note-taking


Pre-task questions helping students reflect upon task requirements and make predictions |
| 6. |
Evaluating own learning and suggesting other ways of learning |
| - |
To help students make plans to learn more effectively in the future, opportunities should be provided for them to reflect upon their learning.
- The teacher showed samples of students’ note sheets on the visualiser. Students discussed, pointed out the good and bad practices in note-taking, and reviewed their own note sheets.
- Students completed a reflection log and reflected upon the strategies used, what was done well and what to improve next.
|
|
Developing self-monitoring skills |
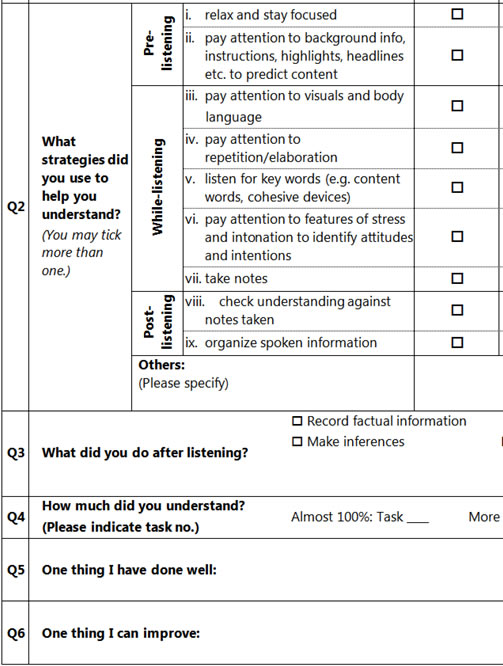
A post-task self-reflection log for evaluating learning and suggesting future learning plans
|
| 7. |
Consolidating and transferring knowledge and skills |
| - |
A range of extended tasks was set to help students apply the taught knowledge and skills in a new context. Students did an extended task of their choice related to the topic. |
| - |
To prepare students for more complex tasks, task management strategies were reinforced throughout the school year. Students were reminded to use note-taking skills when doing other listening tasks. The teachers did not only ask pre-task questions to make students more aware of task requirements, but also asked students to generate pre-task questions by themselves. |
|
Application of learning |

Students applying what they have learned in post-tasks
|

