Topic: Equipping curriculum leaders to support whole school implementation on LAC |
| Objectives: |
| School level: |
| - |
to adopt a whole school approach to make cross-curricular links among different KLAs |
| - |
to formulate a four-year holistic plan to set a clear direction on the planning and implementation of LAC to promote cross-curricular collaboration |
| |
|
| Curriculum level: |
| - |
to make coherence in the school-based curriculum through curriculum mapping across subjects |
| |
|
| Teacher level: |
| - |
to develop subject panel heads’ curriculum leadership skills to support the implementation of LAC |
| - |
to equip teachers’ professional knowledge and skills on the planning and implementation of LAC |
| |
|
| Student level: |
| - |
to increase students’ exposure to English inside and outside classroom through the LAC project at junior secondary levels |
| - |
to enhance students’ motivation in learning content subjects in English through various LAC initiatives (e.g. LAC Days and Cross-curricular Project Learning) |
| - |
to develop students’ academic literacy and generic skills (e.g, critical thinking and independent learning) in different KLAs |
Level
S1-S4
Development of LAC in all subjects within 4 years (2010-2014) |
| |
| Subject |
Yr1 (10-11) |
Yr2 (11-12) |
Yr3 (12-13) |
Yr4 (13-14) |
| English |
S1 |
S1+S2 |
S1-S3 |
S1-S3 |
| Maths |
|
S1 |
S1+S2 |
S1-S3 |
| IS |
S1 |
S1+S2 |
S1+S2 |
S1+S2 |
| Geography |
|
S2 |
S2+S3 |
S2+S3 |
| ICT |
|
|
S1 |
S1+ S2 |
| Physics |
|
|
S3 |
S3 |
| Chemistry |
|
|
S3 |
S3 |
| Biology |
|
|
S3 |
S3+S4 |
| History |
|
S2 |
S2 |
S2 |
| VA |
|
|
|
S1 |
| HE |
|
|
|
S1 |
| Music |
|
|
|
S1 |
Design of the project:
To be able to implement an innovation which is complex in nature and requires close collaboration with different stakeholders, a gradual approach to change management has been adopted. The following diagram shows the emphasis given at each stage.
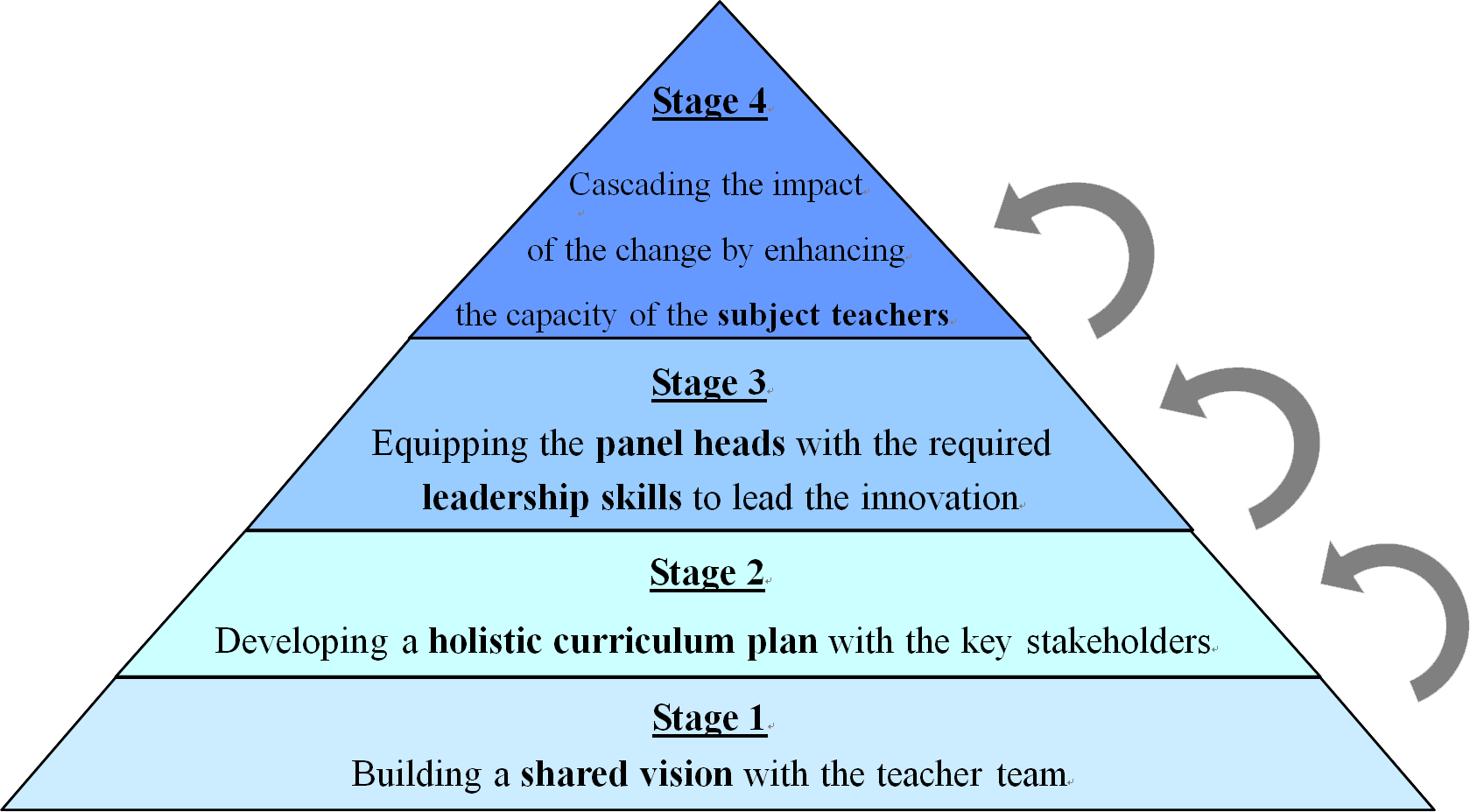
1. Building a shared vision
Successful school improvement requires establishing a clear educational vision and a shared institutional mission (Peterson, K. 1995). Before mobilising the teachers to implement the change, the school management shared with them the background, rationale and objectives behind the implementation of the initiative.
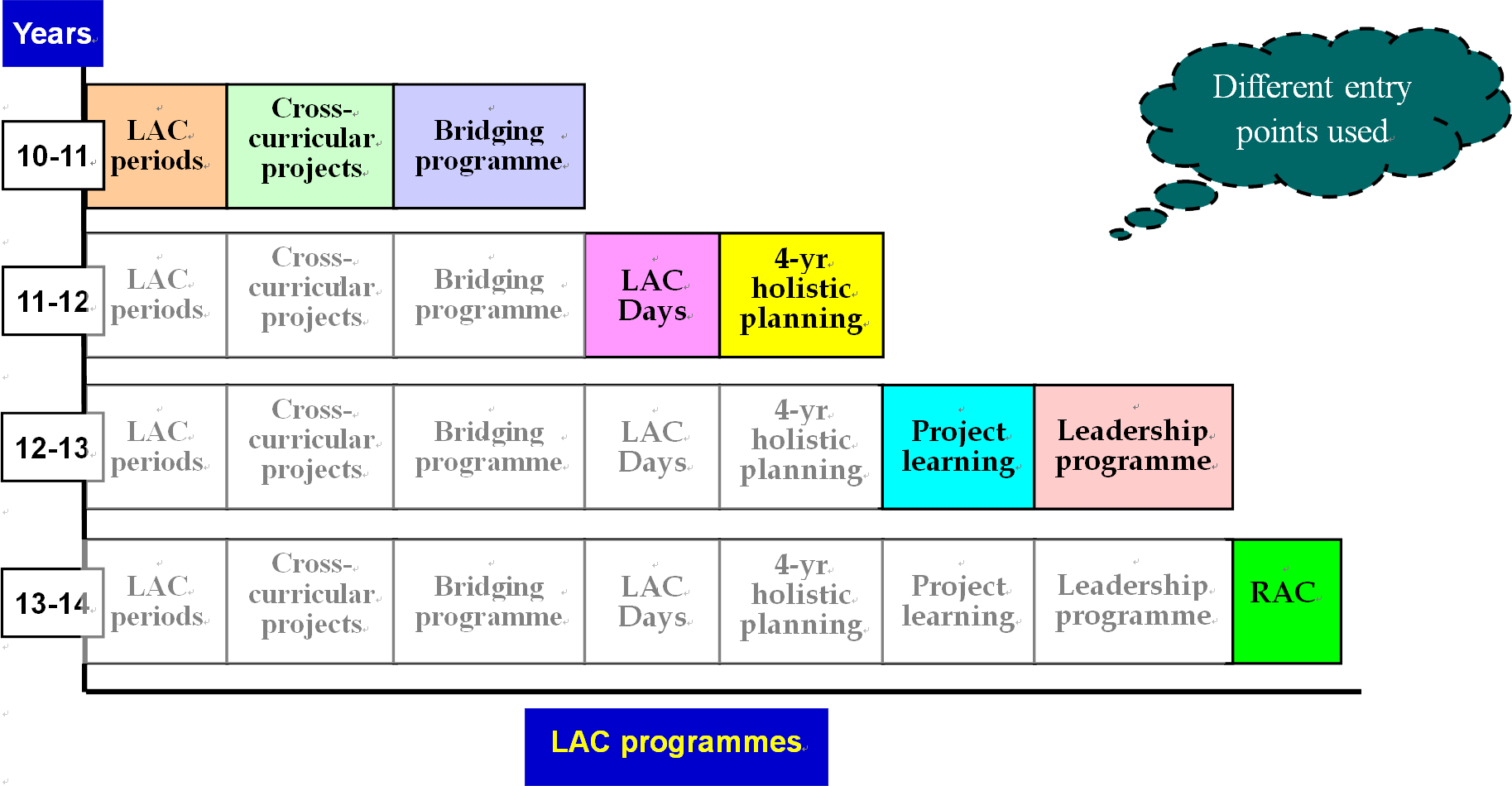
A four-year holistic plan was formulated to give teachers a clear direction on cross-curricular collaboration and planning of different KLAs. This allowed flexibility for the school to implement LAC holistically at a manageable pace. During the past four years, the principal, the LAC co-ordinator and the LLSS officer made concerted efforts on different occasions to raise teachers’ awareness of the importance of supporting student learning through English. This gradually helped build a sense of commitment among teachers and set a clear direction for their future planning. In addition, the clear vision also inspired teachers to think of possible solutions when facing challenges.
2. Developing a holistic curriculum plan with the key stakeholders
The school developed a holistic curriculum plan by adopting a variety of approaches that could address the needs, interests and levels of readiness of different KLAs.. This gave teachers greater flexibility and space to increase students’ motivation and exposure to use English in their own subjects.
3. Helping panel heads develop the required curriculum leadership skills
To accomplish lasting reform, we need leaders who can create a fundamental transformation in the learning cultures of schools and of the teaching profession itself. (Fullan, M. 2002). A three-year leadership training programme was designed to equip the subject panel heads as change agents to initiate the curriculum change through planning, implementation and management of language across the curriculum. The subject panel heads took the lead in setting clear objectives and proposing workable actions, mapping out the curriculum and designing appropriate teaching materials with panel members.
Through working with English teachers, the panel heads were able to guide the panel members to examine the difficulties in using English to learn content subjects, and explore different approaches to maximize students’ opportunities to use English inside and outside the classroom. In addition to that, they shared the difficulties encountered and exchanged ideas & experiences with other panel heads in regular LAC committee meetings. To promote the professional development of panel members, some panel heads organised activities such as lesson study and invited panel members to share their good practices on staff development day.

The Geography and IS panel heads shared the progress of LAC development of their subjects in regular LAC committee meetings.
4.Cascading the impact of the change by enhancing the capacity of the subject teachers
In order to facilitate cross-curricular and inter-departmental collaboration, some communication platforms were established to encourage teachers to exchange ideas and experiences through co-planning, discussion, cross-subject peer lesson observation, regular reporting of work in staff meetings and annual staff development day.

|

|
| Different subjects celebrated their good work on annual staff development day. |
|

