Notes on Genres - Causal Explanation
Function
To explain how something occurs or why such phenomenon happens. Usually it details the various stages and explains the causes for the relevant change(s) involved in an event.
Schematic Structure
Phenomenon Identification ^ Explanation Sequence ^ Conclusion
Examples
2012 DSE 1B Q3b, 2012 DSE 1B Q9a, 2013 DSE 1B Q3b(ii), 2013 DSE 1B Q10b
Common vocabulary and sentence patterns used in setting questions
- Explain why ...... occurs
- Account for ......
- Give reasons for the occurrence of ...
- What causes ......?
- Explain how...
Genre Structure and language features
| Schematic Structure | Contents and Functions | Language features |
|---|---|---|
Phenomenon Identification |
State clearly the things or phenomena to be explained by identifying the causes and effects. |
Use "If..." and "when..." to bring out the condition and cause. Clause "the reason for..." always brings out the following explanation. |
Explanation Sequence |
Explain the various characteristics of things or accounts for the different reasons of the occurrence of the phenomena in paragraphs |
Use words to express the cause and effect, such as "Because", "because of", "due to", "resulting in", "since", "caused by", "leading to", "thus", "hence", "so that"... etc. |
Conclusion (optional) |
Summarize the explanation |
Conjunctions "Therefore", "Hence" and "Thus" always bring out the conclusion |
Example of Causal Explanation writing [Source: HKEAA 2013 DSE 1B Q3b(ii)]
A lift car is going up with constant speed as shown in Figure 1. The upward force raising the lift car is provided by the cable wound on a drum which is driven by a motor. Another counterweight of similar mass of the lift car is installed at the other end of the cable. The counterweight always moves in the opposition direction of the lift car. Assume that there is no slipping between the cable and the drum. Explain the advantage of having the counterweight installed at the other end of the cable.
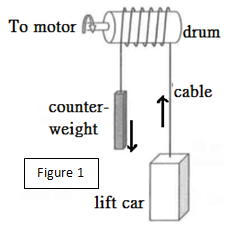
If the counterweight is installed, the required output power of the motor is smaller. The reason is as follows. If the counterweight is installed at the other end of the cable, it will reduce the turning force generated by the motor. Thus, the motor needs less force to move the lift car up as compared with that without counterweight. Therefore, the output power required from the motor is smaller.
 Analysis of Causal Explanation writing
Analysis of Causal Explanation writing
| Schematic Structure | Text | Linguistic Features |
|---|---|---|
Phenomenon Identification |
If the counterweight is installed, the required output power of the motor is smaller. The reason is as follows. |
Use "If" to bring out the cause. Clause "the reason is as follows..." brings out the following explanation. |
Explanation Sequence 1 |
If the counterweight is installed at the other end of the cable, it will reduce the turning force generated by the motor. |
Material process "reduce" describes the function of counterweight. |
Explanation Sequence 2 |
Thus, the motor needs less force to move the lift car up as compared with that without counterweight. |
Material process "needs less" describes the change of work done by the motor. |
Conclusion |
Therefore, the output power required from the motor is smaller. |
Causal conjunction "therefore" brings out the result, identifies the phenomenon again and draws a conclusion. |

