Notes on Genres - Procedural Account
Function
To give accurately an account of a scientific activity including its aim, steps, and results or conclusion in order of the significant events
Schematic Structure
Direction ^ Aim ^ Steps [1-n] ^ Results
Examples
2012 DSE 1B Q10, 2013 DSE 1B Q2a, 2013 DSE 1B Q5
Common vocabulary and sentence patterns used in setting questions
- Describe an experiment to...
- Describe the procedure of...
- Design an experiment using...
Genre Structure and language features
| Schematic Structure | Contents and Functions | Language features |
|---|---|---|
Direction/Aim |
State the aim for performing the procedure, and bring out the succeeding steps (Remark: Though the aim has usually been specified in the question, it will be more complete and clear if it is restated briefly in the answer) |
Quoting the direction as the aim of the procedure Phase "as follows" to bring out the succeeding texts. |
Steps |
Describe the actions in the order they need to be performed, specifying the conditions or precautions as necessary. These may include actions such as operating apparatus / equipment, processing of material, and measurement. May include diagrams, notes or mathematical equation if necessary |
Temporal conjunctions "Firstly", "after that", "then", "next", "finally", "before", "in turn", to indicate different steps Words to illustrate actions more precisely, such as adverbs |
Result |
Responding to the aim and declaring that the aim is thus achieved. |
Conjunctions "as a result", "consequently", "hence" and "thus" to bring out the result / conclusion |
Example of Procedural Account writing (Source: HKEAA DSE 2013 1B Q5)
Figure .1 shows a smooth sloping track ABC firmly fixed in a vertical plane with its horizontal part BC resting on a bench surface. You are given a toy skier, a meter rule and a long rough paper strip with adhesive on the bottom surface.
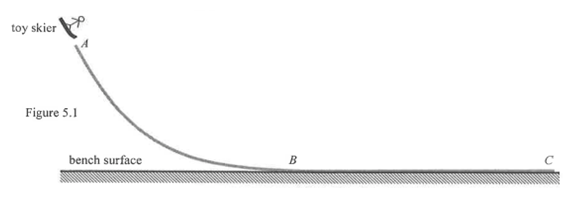
Using the apparatus provided, describe an experiment to study how the stopping distance of the toy skier depends on its height of release. Your description should include the physical quantities to be measured and the result expected. (5 marks)
Procedure of studying how the stopping distance of the toy skier depends on its height of release is as follows: Firstly, stick the paper strip onto the horizontal part BC of the track. Then, release the toy from a certain height h from the bench surface and measure the corresponding stopping distance d from B, the beginning of the horizontal part of the track. After that, release the toy from different heights and measure the corresponding stopping distances. Lastly, plot a graph of d against h. A straight line passing through origin should be obtained, which illustrates that the work done against friction over the distance, d is directly proportional to the potential energy released over the drop in height, h.
 Analysis of Procedural Account writing
Analysis of Procedural Account writing
| Schematic Structure | Text | Linguistic Features |
|---|---|---|
Direction/Aim |
Procedure of studying how the stopping distance of the toy skier depends on its height of release is as follows: |
Quoting the direction as the aim of the procedures. "as follows" brings out the succeeding texts |
Step 1 |
Firstly, stick the paper strip onto the horizontal part BC of the track. |
Temporal conjunction "Firstly" indicates the first step. Material Process "stick" describes the first step. |
Step 2 |
Then, release the toy from a certain height h from the bench surface and measure the corresponding stopping distanced d from B, the beginning of the horizontal part of the track. |
Temporal conjunction "Then" indicates the second step. Circumstance of location "from a certain height h from the bench surface" expresses the location of starting second step. Material Process "release" and "measure" describes the second step. |
Step 3 |
After that, release the toy from different heights and measure the corresponding stopping distances. |
Temporal conjunction "after that" indicates the third step. Circumstance of location "from different heights" expresses the location of conducting the third step. Material Processes "release" and "measure" describe the third step. |
Step 4 |
Lastly, plot a graph of d against h. A straight line passing through the origin should be obtained which illustrates that the work done against friction over the distance, d is directly proportional to the potential energy released over the drop in height, h. |
Temporal conjunction "Lastly" indicates the last step. Material Process "plot" describes the last step. Material Process "obtained" states the expected result. Material Process "illustrates" brings out how d depends on h. |

